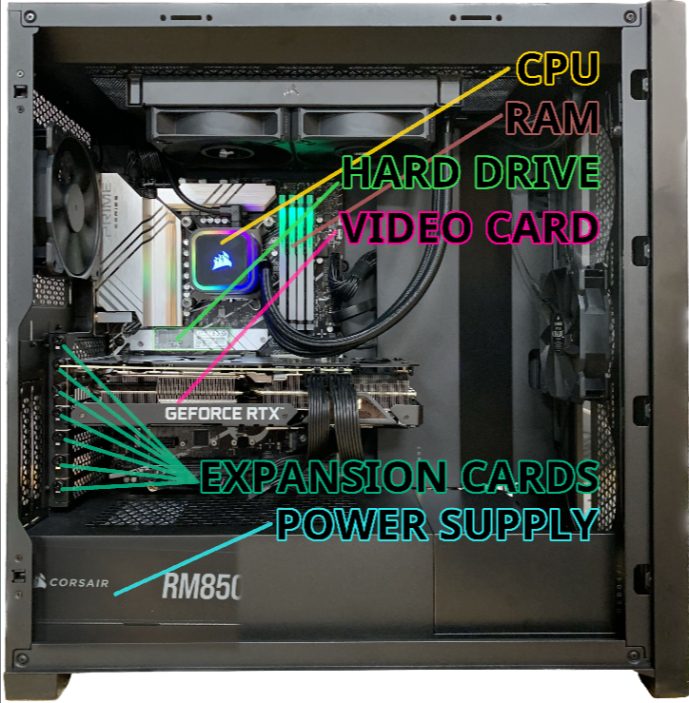

A computer can be broken down into several basic parts:
- Central processing unit (CPU): This is the "brain" of the computer that carries out the instructions of the programs. It's responsible for performing calculations, making decisions, and controlling the other parts of the computer.
- Random access memory (RAM): This is the working memory of the computer where data and programs are temporarily stored while the computer is running. RAM is faster than the computer's hard drive, but it's also more expensive.
- Hard drive: This is the long-term storage device for the computer where files and programs are saved. Unlike RAM, the hard drive retains data even when the computer is turned off.
- Motherboard: This is the main circuit board that connects all the parts of the computer together.
- Power supply unit (PSU): This provides power to the computer's components.
- Input/output (I/O) devices: These include devices such as keyboards, mice, and monitors that allow the user to interact with the computer.
- Expansion cards: These are cards that can be added to the motherboard to add functionality to the computer, such as a graphics card for better video performance or a sound card for better audio.
These are just the basic parts of a computer, and there are many other components and peripherals that can be added or modified depending on the specific needs of the user.
